News
應(yīng)用支持
- 您現(xiàn)在的位置: 首頁 → 應(yīng)用支持 → 應(yīng)用文獻(xiàn)
-

應(yīng)用ASD高光譜遙感技術(shù)監(jiān)測由絲核菌引起的甜菜根腐病和冠腐病
日期:
2015-08-11
瀏覽次數(shù):
47
HYPERSPECTRAL REMOTE SENSING FOR DETECTION OF RHIZOCTONIA CROWN AND ROOT ROT IN SUGARBEET
Gregory J. Reynolds1, Carol E. Windels2, Ian V. MacRae3, and Soizik Laguette4
Graduate Student, Professor, Associate Professor, and Assistant Professor, respectively
1University of Minnesota, Department of Plant Pathology, St. Paul
2University of Minnesota, Department of Plant Pathology and Northwest Research & Outreach Center, Crookston
3University of Minnesota, Department of Entomology and Northwest Research & Outreach Center, Crookston
4University of North Dakota, Department of Earth System Science and Policy, Grand Forks
?
The soilborne fungus Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-2 causes Rhizoctonia crown and root rot (RCRR) of sugarbeet. The pathogen is becoming common and widespread in sugarbeet-growing regions of Minnesota and North Dakota because of increased acreage of soybean, edible bean and corn, which are also infected by R. solani AG-2-2 (5, 23). Thus, inoculum of the fungus is building up in soil and contributing to further outbreaks.
Severity of RCRR typically is assessed by a visual rating scale based on the amount of rot on the taproot. This traditional visual rating system, however, is destructive because entire plants are removed from soil. Furthermore, visual disease assessments are subjective in nature and affected by differences between individuals rating roots caused by fatigue, bias, and human error (13).
Remote sensing is an alternative method to non-destructively assess plant diseases rapidly, repeatedly, and over a large area without physical contact with the sampling unit (e.g., sugarbeet foliage) (13). It is based on measuring reflectance of electromagnetic radiation from a subject of interest, primarily in the visible (390-770 nm), near infrared (770-1300 nm), mid infrared (1300-2500 nm), and thermal infrared (2.5-15 μm) ranges (13). Instruments may collect either hyperspectral or multispectral reflectance data. Hyperspectral sensors measure reflectance contiguously as a series of narrow wavelength bands while multispectral sensors measure reflectance at a few wide bands separated by segments where no measurements are taken (17). Hyperspectral and multispectral wavelength bands obtained for plants typically are used to calculated vegetation indices that provide pertinent information (e.g., chlorophyll content) or to correct for background interference from soil or the atmosphere (21).
Remote sensing technology has been applied to the detection of numerous crop diseases, including Cercospora leaf spot (19) and Rhizomania (20) of sugarbeet. Aboveground symptoms of RCRR, including yellowing of foliage and sudden wilting of leaves, would be the basis for remote detection of this disease, but it also may be possible to detect stress in the plants before visible wilting occurs. Reduced photosynthesis rates or water content in sugarbeet plants could produce changes detectable with remote sensing instrumentation, but not the naked eye. Laudien et al. (10, 11) conducted research to determine the potential of remote sensing to detect RCRR, but the authors focused more on the distinction between healthy and unhealthy plants, rather than on the disease. They detected RCRR at the end of the growing season but did not address population of AG 2-2 (IIIB or IV), early-season detection of the disease, or the relationship of reflectance to severity of RCRR. Early detection of RCRR and/or the ability to assess disease severity based on remote sensing will allow assessment of entire fields for disease management.
Severity of RCRR typically is assessed by a visual rating scale based on the amount of rot on the taproot. This traditional visual rating system, however, is destructive because entire plants are removed from soil. Furthermore, visual disease assessments are subjective in nature and affected by differences between individuals rating roots caused by fatigue, bias, and human error (13).
Remote sensing is an alternative method to non-destructively assess plant diseases rapidly, repeatedly, and over a large area without physical contact with the sampling unit (e.g., sugarbeet foliage) (13). It is based on measuring reflectance of electromagnetic radiation from a subject of interest, primarily in the visible (390-770 nm), near infrared (770-1300 nm), mid infrared (1300-2500 nm), and thermal infrared (2.5-15 μm) ranges (13). Instruments may collect either hyperspectral or multispectral reflectance data. Hyperspectral sensors measure reflectance contiguously as a series of narrow wavelength bands while multispectral sensors measure reflectance at a few wide bands separated by segments where no measurements are taken (17). Hyperspectral and multispectral wavelength bands obtained for plants typically are used to calculated vegetation indices that provide pertinent information (e.g., chlorophyll content) or to correct for background interference from soil or the atmosphere (21).
Remote sensing technology has been applied to the detection of numerous crop diseases, including Cercospora leaf spot (19) and Rhizomania (20) of sugarbeet. Aboveground symptoms of RCRR, including yellowing of foliage and sudden wilting of leaves, would be the basis for remote detection of this disease, but it also may be possible to detect stress in the plants before visible wilting occurs. Reduced photosynthesis rates or water content in sugarbeet plants could produce changes detectable with remote sensing instrumentation, but not the naked eye. Laudien et al. (10, 11) conducted research to determine the potential of remote sensing to detect RCRR, but the authors focused more on the distinction between healthy and unhealthy plants, rather than on the disease. They detected RCRR at the end of the growing season but did not address population of AG 2-2 (IIIB or IV), early-season detection of the disease, or the relationship of reflectance to severity of RCRR. Early detection of RCRR and/or the ability to assess disease severity based on remote sensing will allow assessment of entire fields for disease management.
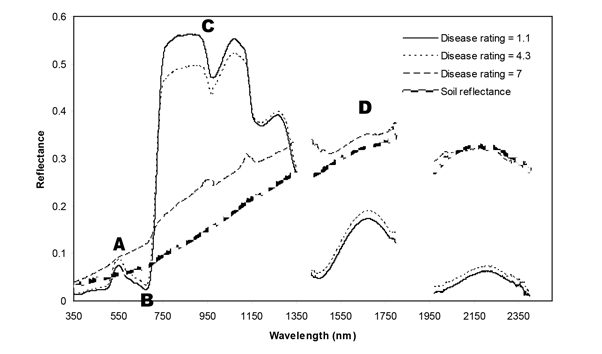
Examples of spectral signatures for soil background reflectance and sugarbeet canopy reflectance in plots with Rhizoctonia crown and root rot disease ratings of 1.1, 4.3, and 7 for the partially resistant variety (data collected August 18, 2008) where A.) is green reflectance (495-570 nm), B.) is red reflectance (620-750 nm), C.) is near infrared reflectance (770-1300 nm), and D.) is mid infrared reflectance (1300-2500 nm).
?
查看原文:
2024
-
09
-
30
沿海鹽沼生態(tài)系統(tǒng)是一種位于海洋與陸地交界處的生物多樣性豐富的獨特生態(tài)環(huán)境。它不僅具有重要的生態(tài)功能,在碳儲存、環(huán)境凈化和防風(fēng)護(hù)堤方面發(fā)揮著重要作用,還對人類社會活動有著極大的支持和調(diào)節(jié)作用。氨氣是大氣環(huán)境中含量豐富的堿性氣體,其在沿海鹽沼生態(tài)系統(tǒng)中的作用不可忽視。但是,過量的氨氣輸入也給其帶來了一系列問題。沿海鹽沼生態(tài)系統(tǒng)NH3源和匯研究背景介紹氨(NH3)是大氣中含量最多的堿性氣體。在氣溶膠形成中發(fā)揮重要作用,而氣溶膠會對人類健康產(chǎn)生不利影響,同時會降低能見度,改變地球輻射平衡,并通過大氣沉積促進(jìn)活性氮(Nr)的全球再分配。農(nóng)業(yè)集約化是NH3的主要人為來源,導(dǎo)致進(jìn)入生物圈的Nr增加一倍。NH3的其他來源包括工業(yè)過程、車輛排放及土壤和海洋的揮發(fā)。農(nóng)業(yè)和城市源通過大氣沉積過程直接或間接排放NH3,其會改變鹽沼的結(jié)構(gòu)和功能。此外,大氣沉積過程是NH3進(jìn)入沿海水域的主要途徑, NH3沉積到敏感的...
2024
-
09
-
30
棕色碳(BrC)是一類在近紫外和可見光區(qū)吸收光輻射的有機(jī)碳,不僅對大氣造成輻射強(qiáng)迫,更是對大氣光化學(xué)反應(yīng)速率有著重要作用。BrC不僅影響著大氣的輻射平衡和氣候變化,還直接關(guān)系到區(qū)域空氣質(zhì)量與公眾健康。本論深入探討了棕色碳發(fā)色團(tuán)的光學(xué)性質(zhì)與化學(xué)成分之間的密切關(guān)聯(lián),為更準(zhǔn)確地評估其在環(huán)境系統(tǒng)中的行為和影響提供了科學(xué)依據(jù)。棕色碳發(fā)色團(tuán)光學(xué)性質(zhì)和化學(xué)成分之間的聯(lián)系背景介紹棕色碳(BrC)是大氣有機(jī)氣溶膠的重要組分,在紫外到近紅外波段具有較強(qiáng)的吸光能力,對全球氣候變化和大氣化學(xué)過程具有重要影響。BrC結(jié)構(gòu)復(fù)雜、種類眾多、來源廣泛。大量研究表明生物質(zhì)燃燒、煤燃燒、機(jī)動車尾氣、生物排放以及二次有機(jī)氣溶膠等是BrC的重要來源。芳香族揮發(fā)性有機(jī)化合物,如苯同系物和衍生物,也可能是BrC發(fā)色團(tuán)的重要前體。但是,不同源排放的BrC進(jìn)入大氣后,受到復(fù)雜的大氣化學(xué)過程,其光學(xué)性質(zhì)和化學(xué)結(jié)構(gòu)會發(fā)生很大的變化。研究方法...
2024
-
06
-
11
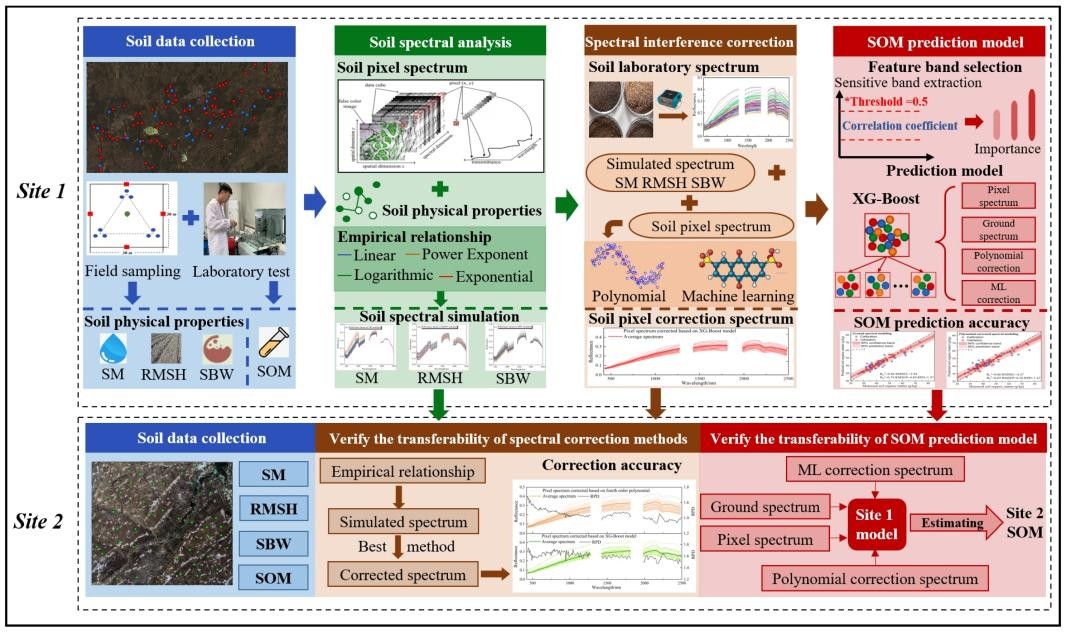
摘要土壤有機(jī)質(zhì)(SOM)在全球碳循環(huán)中起著非常重要的作用,而高光譜遙感已被證明是一種快速估算SOM含量的有前景方法。然而,由于忽略了土壤物理性質(zhì)的光譜響應(yīng),SOM預(yù)測模型的準(zhǔn)確性和時空可遷移性較差。本研究旨在通過減少土壤物理性質(zhì)對光譜的耦合作用來提高SOM預(yù)測模型的時空可遷移性?;谛l(wèi)星高光譜圖像和土壤物理變量,包括土壤濕度(SM)、土壤表面粗糙度(均方根高度,RMSH)和土壤容重(SBW),建立了基于信息解混方法的土壤光譜校正模型。選取中國東北的兩個重要糧食產(chǎn)區(qū)作為研究區(qū)域,以驗證光譜校正模型和SOM含量預(yù)測模型的性能和可遷移性。結(jié)果表明,基于四階多項式和XG-Boost算法的土壤光譜校正具有優(yōu)異的準(zhǔn)確性和泛化能力,幾乎所有波段的殘余預(yù)測偏差(RPD)均超過1.4。基于XG-Boost校正光譜的SOM預(yù)測精度最 高,決定系數(shù)(R2)為0.76,均方根誤差(RMSE)為5.74 g/kg,...
2024
-
05
-
20
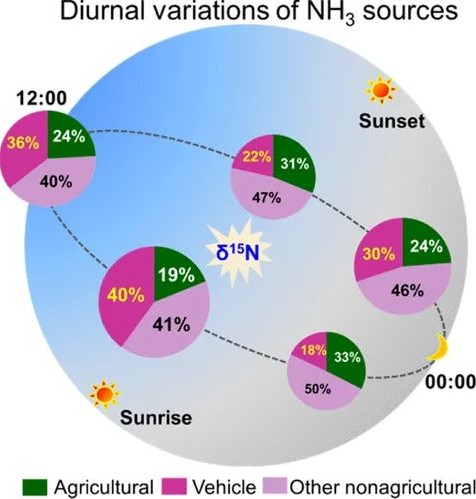
北京,這座擁有千年歷史的城市,見證了無數(shù)歷史的變遷和現(xiàn)代文明的飛躍。然而,隨之而來的是空氣質(zhì)量問題,尤其是由機(jī)動車尾氣排放引發(fā)的大氣污染。據(jù)相關(guān)研究顯示,機(jī)動車尾氣中含有大量的有害物質(zhì),包括一氧化碳、氮氧化物、揮發(fā)性有機(jī)化合物以及細(xì)顆粒物等,這些污染物不僅對人體健康構(gòu)成威脅,還會導(dǎo)致城市霧霾的形成,影響城市的視覺美感和居民的生活質(zhì)量。在眾多污染物中,氨氣作為一種典型的堿性氣體,其來源多樣,包括農(nóng)業(yè)活動、工業(yè)生產(chǎn)、生活垃圾處理等。在北京市城區(qū)車輛排放是否是氨氣的主要來源?據(jù)此,來自中國科學(xué)院大氣物理研究所的研究團(tuán)隊進(jìn)行了相關(guān)研究。北京城區(qū)NH3排放源-機(jī)動車尾氣背景介紹氨氣是大氣中重要的堿性氣體,在中和酸性氣體,形成二次氣溶膠方面發(fā)揮著重要作用。NH3在大氣中滯留時間短,因此NH3濃度日變化顯著。一般特征為在早上大約07:00~10:00,NH3濃度到達(dá)峰值。然而以前的研究局限于單一季節(jié),無...
【關(guān)閉窗口】【打印】
北京理加聯(lián)合科技有限公司
地址:北京市海淀區(qū)安寧莊東路18號光華創(chuàng)業(yè)園5號樓(生產(chǎn)研發(fā))
光華創(chuàng)業(yè)園科研樓四層
光華創(chuàng)業(yè)園科研樓四層
電話:13910499761 13910499762 010-51292601
傳真:010-82899770-8014
郵箱:info@li-ca.com
郵編:100085
地址:深圳市寶安區(qū)創(chuàng)業(yè)二路玖悅雅軒商業(yè)裙樓3層瑞思BEEPLUS 3029室
手機(jī):13910499772
- 您的姓名:
- *
- 公司名稱:
- *
- 地址:
- *
- 電話:
- *
- 傳真:
- *
- 電子郵箱:
- *
- 郵政編碼:
- *
- 留言主題:
- *
- 詳細(xì)說明:
- *
在線留言
關(guān)注我們
 官方微信
官方微信
 官方手機(jī)端
官方手機(jī)端
友情鏈接: